选择排序(Selection Sort)原理介绍
2 S, V1 x- a+ ^# Q) G; S) |选择排序(Selection Sort)是一种简单的排序算法,其实现原理如下:
, \2 \8 n7 D+ D/ f7 X& U. |( t遍历待排序数组,从第一个元素开始。
. L2 }( b. v# S- p) L( _假设当前遍历的元素为最小值,将其索引保存为最小值索引(minIndex)。
( a: i* z7 s- m" F! a2 j! @( _3 b在剩余的未排序部分中,找到比当前最小值还要小的元素,并更新最小值索引。
2 E& S2 \/ ` A* l9 N在遍历结束后,将找到的最小值与当前遍历位置的元素进行交换。
' q3 u- j+ \ P" B+ ^4 I% e0 R$ E! k重复步骤2至4,直到排序完成。) G+ P0 H+ w; Q8 s" c* w' m
C#代码实现# A3 L6 R* |) V, ?
/// <summary>
/// 选择排序算法
/// </summary>
public static void SelectionSortAlgorithmMain()
{
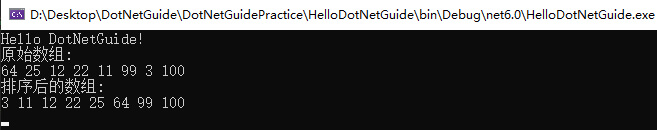
int[] array = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11, 99, 3, 100 };
Console.WriteLine("原始数组: ");
PrintArray(array);
SelectionSortAlgorithm(array);
Console.WriteLine("排序后的数组: ");
PrintArray(array);
}
static void SelectionSortAlgorithm(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// 在未排序部分中找到最小元素的索引
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
{
minIndex = j;
}
}
// 将最小元素与未排序部分的第一个元素交换位置
int temp = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
static void PrintArray(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
. h; r3 i! n% d. W( m( v总结
0 M8 Z; | _8 G/ Z* P: D# s$ N选择排序算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2),其中n是待排序数组的大小。尽管其时间复杂度较高,但选择排序算法比较简单易懂,并且在某些特定情况下,例如对于小规模的数组来说,其性能可能表现得比其他高级排序算法要好。 |  |手机版|小黑屋|paopaomj.COM
(
|手机版|小黑屋|paopaomj.COM
( ![]() 渝ICP备18007172号|
渝ICP备18007172号|![]() 渝公网安备50010502503914号 )
渝公网安备50010502503914号 )